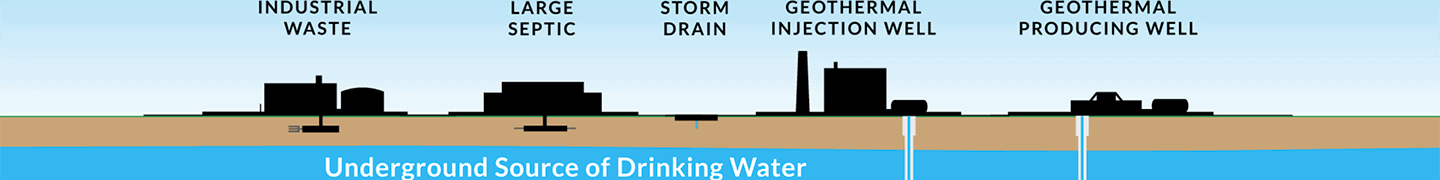
EPA regulations define wells that do not fit into any other category as Class V wells. As such, Class V contains both shallow and deep systems injecting fluids above, into and below underground sources of drinking water. These wells inject non-hazardous fluids underground. Some operational uses for Class V wells include storm water drainage wells, septic system leach fields, agricultural drainage wells, aquifer storage and recovery wells, and geothermal electric power wells. Class V are the most numerous regulated injection wells with over half a million wells in the United States.1USEPA. (2022, December 19). Class V wells for injection of non-hazardous fluids into or above underground sources of drinking water. Retrieved 12/30/2022 from https://www.epa.gov/uic/class-v-wells-injection-non-hazardous-fluids-or-above-underground-sources-drinking-water.
Underground Injection Wells by Class
| Injection Well Class | Number of Injection Wells | Injection Wells Inspected |
|---|---|---|
| Class I | 830 | 453 |
| Class II | 181,431 | 84,317 |
| Class III | 28,327 | 406 |
| Class IV | 122 | 27 |
| Class V | 531,176 | 4,038 |
| Class VI | 2 | 0 |
Source: EPA2USEPA. (2020). Underground Injection Control Program Fact Sheet. EPA 816F19005 April 2020.
The majority of the different kinds of Class V wells rely on gravity drainage. For example, gravity pulls fluids through floor drains to septic systems or dry wells in facilities such as gas stations, service stations, and car washes. Municipal storm drains that lead to dry wells also use gravity to pull water off roads.3USEPA. (2022, December 19). Class V wells for injection of non-hazardous fluids into or above underground sources of drinking water. Retrieved 12/30/2022 from https://www.epa.gov/uic/class-v-wells-injection-non-hazardous-fluids-or-above-underground-sources-drinking-water.
Due to the diversity of Class V wells, there is no standard construction or geological requirement. However, the well’s relationship or proximity to the aquifer influences how it should be managed. Because operations for Class V wells generally do not treat fluids before discharge or injection, proper management of these facilities is the only way to protect underground sources of drinking water.4USEPA. (2022, December 19). Class V wells for injection of non-hazardous fluids into or above underground sources of drinking water. Retrieved 12/30/2022 from https://www.epa.gov/uic/class-v-wells-injection-non-hazardous-fluids-or-above-underground-sources-drinking-water.

Images: “Graphic” by Top Energy Training